Are you looking for an essay on ‘Photovoltaic Power System’? Find paragraphs, long and short essays on ‘Photovoltaic Power System’ especially written for school and college students.
Essay on Photovoltaic Power System
Essay Contents:
- Essay on the Introduction to Photovoltaic Cell
- Essay on the Historical Background of Photovoltaic Generators
- Essay on the Basic Photovoltaic System for Power Generation
- Essay on the Limitations of Photovoltaic Energy Converters
- Essay on the Fabrication of Photovoltaic Cells
- Essay on the Advantages and Disadvantages of Photovoltaic Solar Energy Conversion
Essay # 1. Introduction to Photovoltaic Cell:
Solar energy can be directly converted to electrical energy by means of photovoltaic effect which is defined as the generation of an electromotive force as a result of the absorption of ionizing radiation. Energy conversion devices which are employed to convert sunlight into electricity by the use of the photovoltaic effect are called solar cells.
A single converter cell is called a solar cell or a photovoltaic cell. To increase the electrical power output a number of such cells are combined and the combination is called a ‘solar array’ or ‘solar module’.
In a photovoltaic cell sensitive element is a semiconductor (not metal) which generates voltage in proportion to the light or any radiant energy incident on it. The most commonly used photovoltaic cells are barrier layer type like iron-selenium cells or Cu-CuO2 cells.
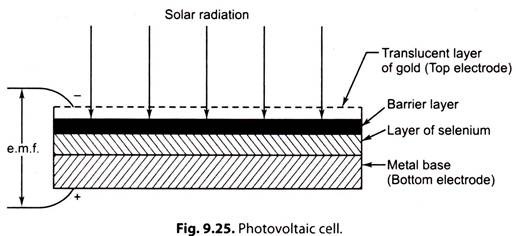
Fig. 9.25 shows a typical widely used photovoltaic cell-“Selenium cell”. It consists of a metal electrode on which a layer of selenium is deposited; on the top of this a barrier layer is formed which is coated with a very thin layer of gold. The latter serves as a translucent electrode through which light can impinge on the layer below. Under the influence of this light, a negative charge will build up on the gold electrode and a positive charge on the bottom electrode.
Photovoltaic cells are widely used in the following fields:
(i) Automatic control systems.
(ii) Television circuits.
(iii) Sound motion picture and reproducing equipment.
Essay # 2. Historical Background of Photovoltaic Generators:
Edmond Becquerel in 1839 noted that a voltage was developed when light was directed onto one of the electrodes in an electrolytic solution. The effect was first observed in a solid in 1877 by W.G. Adams and R.E. Day, who conducted experiments with selenium.
Other early workers with solids included Schottky, Lange and Grandahl, who did pioneering work in producing photovoltaic cells with selenium and cuprous oxide. This work led to the development of photoelectric exposure meters. 1954 researchers turned to the problem of utilizing the photovoltaic effect as a source of power.
In that year several groups including the workers at Bell Telephone Laboratories achieved conversion efficiencies of about 6 per cent by means of junctions of P-type and N-type semiconductors. These early junctions, commonly called P-N junctions, were made of cadmium sulphide and silicon. Later workers in the area have achieved efficiencies more than 20 per cent by using improved silicon P-N junctions etc.
Essay # 3. Basic Photovoltaic System for Power Generation:
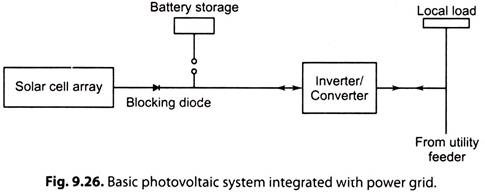
Fig. 9.26. shows a basic photovoltaic system integrated with the utility grid. With the help of this system the generated electrical power can be delivered to the local load.
This system consists of the following:
1. Solar Array:
The solar array (large or small) converts the insolation to useful D.C. electrical power.
2. Blocking Diode:
The blocking diode confines the electrical power generated by the solar array to flow towards the battery or grid only. In the absence of blocking diode the battery would discharge back (through the solar array) during the period when there is no insolation.
3. Battery Storage:
Battery storage stores the electrical power generated through solar array.
4. Inverter/Converter:
Inverter/converter (usually solid state) converts the battery bus voltage to A.C. of frequency and phase to match that needed to integrate with the utility grid. Thus it is typically a D.C, A.C. inverter.
5. Switches and Circuit Breakers:
Switches and circuit breakers permit isolating parts of the system, as the battery.
Essay # 4. Limitations of Photovoltaic Energy Converters:
The major factors which prohibit real photovoltaic converters from achieving the higher efficiencies are:
1. Reflection losses on the surface.
2. Incomplete absorption.
3. Utilization of only part of the photon energy for creation of electron hole pairs.
4. Incomplete collection of electron-hole pairs.
5. A voltage factor.
6. A curve factor related to the operating unit at maximum power.
7. Additional delegation of the curve due to internal series resistance.
Essay # 5. Fabrication of Photovoltaic Cells:
A. Silicon Cells:
Silicon cells are most widely used. Next to oxygen, silicon is the most abundant element on earth. The pure silicon used in cell manufacture is extracted from sand which is mostly silicon dioxide (Si02). The silicon required for solar cell use, because of its high purity, is expensive.
The fabrication of silicon cells includes the following steps:
(i) The pure silicon is placed in an induction furnace where boron is added to melt. This turns the crystal resulting from the melt into p-type material.
(ii) A small seed of single crystal silicon is dipped into the melt and withdrawn at a rate slower than 10 cm per hour, the resulting inset looks like a medium sized carrot. The rate of growth and other conditions are adjusted so that the crystal that is pulled is a single crystal.
(iii) Wafers are then sliced from the grown crystal by the use of a diamond cutting wheel. The slices are then lapped, generally by hand, to remove the saw marks and strained regions.
(iv) After a fine lap the slabs are etched in hydrofluoric acid or nitric acid to complete the first phase of preparation of the cells. We now have thin slices of p-type silicon with a carefully finished surface.
(v) The wafers are then sealed in a quartz tube partly filled with phosphorous pentoxide and the arrangement is placed in a diffusion furnace where temperature is carefully controlled; this process causes the phosphorous to diffuse into the P-type silicon to a depth of about 10–4 cm to 10–5 cm.
(vi) The cells are then etched in a concentrated acid to remove unwanted coatings that formed during manufacture. Wax or Teflon masking tape is used to protect the surfaces not to be etched.
B. Thin Film Solar Cells:
These cells have the following advantages:
(i) The material cost is low.
(ii) The manufacturing cost is low (possibly avoiding the need for single crystal growth).
(iii) High power-to-weight ratios.
(iv) Low array costs, because the number of connections needed will be greatly reduced.
The example of this type of cell is cadmium sulphide (CdS) cells. CdS cells having areas of 50 cm2 have been made by evaporating the semiconductor on to a flexible substrate such as kapton, a metallized plastic substrate. A barrier layer of copper sulphide is then deposited on top of the CdS. Power to weight ratios of 200 watts/kg are claimed for such cells. These cells have low efficiency and instability.
Essay # 6. Advantages and Disadvantages of Photovoltaic Solar Energy Conversion:
Advantages of Photovoltaic Solar Energy Conversion:
(i) There are no moving parts.
(ii) Solar cells are easy to operate and need little maintenance.
(iii) They have longer life.
(iv) They are highly reliable.
(v) They do not create pollution problem.
(vi) Their energy source is unlimited.
(vii) They can be fabricated easily.
(viii) They have high power to weight ratio.
(ix) They can be used with or without sun tracking, making possible a wide range of application possibilities.
(x) They have ability to function unattended for long periods as evident in space programme.
Disadvantages of Photovoltaic Solar Energy Conversion:
(i) The cost of a solar cell is quite high.
(ii) The output of a solar cell is not constant it varies with the time of day and weather.
(iii) Amount of power generated is small.