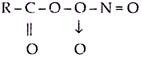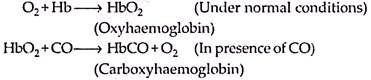Here is a compilation of essays on ‘Air Pollution’ for class 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12. Find paragraphs, long and short essays on ‘Air Pollution’ especially written for school and college students.
Essay on Air Pollution
Essay Contents:
- Essay on the Introduction to Air Pollution
- Essay on the Facts about Air Pollution
- Essay on the Causes of Air Pollution
- Essay on the Classification of Factors Causing Air Pollution
- Essay on the Air Pollutants Gases
- Essay on the Particulate Pollutants
- Essay on the Effects of Air Pollution on Humans
- Essay on the Prevention of Air Pollution
- Essay on the Air Pollution Control Equipment
Essay # 1. Introduction to Air Pollution:
Dust, dirt, harmful gases and industrial emissions, all form part of what is called air pollution. These pollutants cause deterioration in air quality and are capable of harming life forms. Air pollution is a serious problem and can be eased with some simple solutions.
When was the last time you stepped out of your house and inhaled clean and fresh air that really invigorated all your senses? Here’s a look at some of the causes of air pollution that has resulted in the thick smog which most city dwellers are subjected to.
Air pollution is a condition triggered by the presence of air-borne pollutants that affect the quality of air we inhale. These pollutants could either be the result of chemical emissions or the particulate material from biological waste. The condition has reached alarming proportion in the modern world, with large scale industrialization and vehicle-emissions being the primary culprits. The pollutants that are air borne cause a lot of harm to humans and animals, other than permanent damage to the natural environment.
Air pollution is something that we cannot really ignore now-a-days. This is evident from the moment we step out of our house and are greeted with black colored smog that hits us directly reminding us that breathing clean air is more of a distant dream. It is so easy for us to endlessly rant and rave about the causes of air pollution and its ill effects, but little do we realize that each person is responsible for all the causes of air pollution and the situation that we face today.
Take a look around you at the dismal state of affairs. The thick smog that is seen in the morning hours is not really due to somebody else but rather due to each and every one of us. Here is a look at the causes of air pollution and how it can affect us if the matter is not taken care of at this stage itself.
Essay # 2. Facts about Air Pollution:
Here are a few reports that have come out recently about the adverse effects of air pollution which will make you sit up and sniff the air around you apprehensively:
i. According to a study, living in a major city places people at a higher risk than living in the radioactive zone in Chernobyl.
ii. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), about 2 million premature deaths are caused each year due to air pollution in cities across the world.
iii. A recent study has revealed that exposure to fine particle matter in polluted air increases the risk of hospitalization due to respiratory and cardiovascular diseases.
iv. According to a German study, people who breathe in the fumes of heavy traffic regularly have higher chances of getting hardening of the arteries, which is associated with the risk of heart attack.
v. A Scottish study has shown that jogging with traffic around results in reduced blood flow to the heart. This is particularly dangerous for people with stable heart disease, because it can trigger off cardiac arrhythmia or even a heart attack.
vi. According to a study conducted on eight-year-olds in Mexico City, being exposed for a long time to high levels of polluted air reduces lung function and growth in children.
vii. According to a 20-year study conducted on the residents of Los Angeles, it has been shown that the adverse effects of air pollution have been grossly underestimated. The researchers opine that chronic health problems due to particulate matter in the air may be double or even triple times greater than the estimates available currently.
So what is air pollution and why is it so harmful? Air pollution is caused when it gets filled with too much gases, particulate matter, and droplets of liquid. In cities, the air gets polluted by the exhaust fumes of vehicles, along with the pollutants given off by construction work and industry. In the country, the dust given off by tractors working on fields, vehicles being driven on gravel or dirt tracks, smoke given off by crop and wood being burnt, and work carried out in rock quarries, are some of the causes of air pollution.
Another major air pollutant in cities is ozone that occurs at ground level. Ozone forms when nitrous oxides and hydrocarbons react with sunlight. However, not everything about ozone is bad. In fact, its presence in the upper atmosphere is beneficial because it keeps out harmful ultraviolet rays, which is one of the major causes of skin cancer. Ozone only becomes problematic when it occurs near the ground where it can be inhaled. When inhaled, ozone causes reduced lung capacity, choking, and coughing.
When the air is polluted, it causes irritation of the throat, lungs and eyes. Some of the common symptoms are- a burning sensation in the eyes, tightness in the chest, and coughing. It exacerbates respiratory conditions like emphysema and asthma, and reduces the body’s capacity to fight off infections of the respiratory system. Also, people afflicted with heart disease, like angina, are usually very sensitive to air pollution. People who exercise outdoors are also susceptible to the symptoms of air pollution, because it involves deeper and faster breathing.
In fact, polluted air is particularly detrimental to those who have lung and/or heart disease. When the pollution levels become very high, it can lead to them having to curtail their activities and even result in hospitalization. Severe air pollution has even been known to cause death in the recent past. However, such high levels of pollution are now not as common in the US.
Another group that is susceptible to the effects of air pollution is children. When they live in areas that have high levels of pollution, children tend to be prone to illnesses like ear aches and bronchitis.
Although some groups of people feel the effects of air pollution more acutely, one of the positive factors is that when there is an improvement in the quality of air, the symptoms caused by air pollution are quickly alleviated for most people who are healthy.
The long-term effects of being exposed to low air pollution levels are still being studied.
Here are some of the ways you can prevent the harmful effects of air pollution affecting you and your family:
i. Try staying indoors as much as possible in the daytime. Usually the air indoors is less polluted than outdoors.
ii. If you cannot avoid going outside, try to do it in the early morning or after sunset. This is particularly important when there are high levels of ozone, which is usually the case in many big cities, because sunshine triggers off the creation of ozone.
iii. When the pollution levels are high, try not to exert yourself. The harder you breathe, the more polluted air you inhale into your lungs.
The above steps should be enough to protect you against air pollution if you are healthy. However, in case you work or live near some source of pollution, or if you are afflicted with chronic lung or heart problem, it is best to seek medical advice on the best ways to deal with it.
Essay # 3. Causes of Air Pollution:
Carbon dioxide is one the main pollutants that causes air pollution. This is because, although living beings do exhale carbon dioxide, this gas is harmful when emitted from other sources, which are caused due to human activity. An additional release of carbon dioxide happens due to various such activities. Carbon dioxide gas is used in various industries such as the oil industry and the chemical industry. The manufacturing process of most products would require the use of this gas.
There are various human activities that add to the increased proportions of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. The combustion of fossil fuels and the harmful effects of deforestation have all contributed towards the same, show that amongst the various gases emitted during a volcanic eruption, carbon dioxide remains to be at least 40% of the emission. Scientists have now therefore identified carbon dioxide as one of those elements that have contributed to global warming.
Causes of air pollution are not limited to this. The combustion of fuels in automobiles, jet planes etc. all cause the release of several primary pollutants into the air. The burning of fossil fuels in big cities which is seen at most factories, offices and even a large number of homes, it is no wonder that air pollution is increasing at an alarming rate.
The release of other harmful gases all adds to the state that we see today. Although carbon dioxide plays an important role in various other processes like photosynthesis, breathing an excess of the same also causes harmful effects towards one’s health.
The various causes of air pollution that releases harmful gases into the atmosphere are caused due to the increasing number of power plants and manufacturing units or industries that mostly have activities related to the burning of fuels. Besides, most automobiles, marine vessels, activities that involve the burning of wood, fumes that are released from aerosol sprays, military activities that involve the use of nuclear weapons, all are the numerous causes of air pollution.
Carbon monoxide is another such gas which, although was present in the atmosphere earlier, is now considered to be a major pollutant. An excess of the same has a harmful effect on our system. There are many reasons why carbon monoxide can be released into the atmosphere as a result of human activities. This is also produced due to any fuel burning appliance and appliances such as gas water heaters, fireplaces, woodstoves, gas stoves, gas dryers, yard equipments as well as automobiles, which add to the increased proportion of this gas into the atmosphere.
Sulfur dioxide is yet another harmful pollutant that causes air pollution. Sulfur dioxide is emit ted largely to the excessive burning of fossil fuels, petroleum refineries, chemical and coal burning power plants etc. Nitrogen dioxide when combined with sulfur dioxide can even cause a harmful reaction in the atmosphere that can cause acid rain.
Nitrogen dioxide is one more gas that is emitted into the atmosphere as a result of various human activities. An excess of nitrogen dioxide mainly happens due to most power plants seen in major cities, the burning of fuels due to various motor vehicles and other such sources, whether industrial or commercial that cause the increase in the levels of nitrogen dioxide.
These and a number of other hazardous air pollutants are emitted with the various numbers of activities that we carry out during the day which are the main causes of air pollution.
Essay # 4. Classification of Factors Causing Air Pollution:
1. Classification on the Basis of Physical States of Air Pollutant:
(a) Gases:
Which freely mix with air without settling down. These are SO2, SO3, NOx, H2S, CO2, O3, HF, aerosols, hydrocarbons and photochemical oxidants.
(b) Particulates:
Small solid particles and liquid droplets are collectively known as particulates, e.g., dust, smoke, smog, asbestos, lead, Hg and cadmium, mist, oil and grease etc.
(c) Deforestation.
(d) Internal combustion engines.
2. Classification on the Basis of Origin:
(i) Primary air pollutants which are directly emitted into the atmosphere and are found as such e.g., CO, NO2, SO2 and hydrocarbons.
(ii) Secondary air pollutants which are derived from the primary pollutants due to chemical or photochemical reaction in the atmosphere e.g., O3, peroxyactylnitrate (PAN) and photochemical smog etc.
3. Classification on the Basis of Chemical Composition:
(i) Organic pollutants, e.g., hydrocarbons, aldehydes, ketones, amines and alcohols.
(ii) Inorganic Pollutants:
(a) Carbon compounds, (CO, CO2 and carbonates).
(b) Nitrogen compounds (NO and NH3)
(c) Sulphur compounds (SO2, H2S, SO3 and H2SO4)
(d) Halogen compounds (HF, HCl, MFX where M is a metal and x is the valency of M).
(e) Oxidizing agents (O3).
4. Classification on the Basis of Major Sources of Air Pollution:
(i) Natural Sources:
The natural sources of air pollution are volcanic eruptions releasing poisonous gases, forest fires, natural organic and inorganic decay or vegetative decay, marsh gases, deflation of sand and dust, extra-terrestrial bodies, cosmic dust, pollen grains of flowers, soil debris, and fugitive spores.
(ii) Man Made Sources:
Man made sources such as increase in pollution, deforestation, burning of fossil fuels, emissions from vehicles, rapid industrialization, agricultural activities and wars, are the major causes of air pollution.
(iii) Emissions of Major Industrial Air Pollutants:
The major air polluting sources are sulphuric acid industry (emits SO3 and SO2), nitric acid plants (oxides of nitrogen), fluoride industry (HF and cryolite), chloroalkali plants (Cl2 and H2 gas, CO and CO2), hydrochloric industry (toxic chlorine and chlorine monoxide), iron and steel industries, radioactive natural sources, phosphoric acid plants, petrochemical refineries (kerosene, gasoline, formaldehyde and fuel oil), power plants.
(iv) Aerosol Pollutants:
These air pollutants remain suspended in air and consist of fine particles of different organic and inorganic compounds having diameter less than 100 μ.
(v) Metallic Contaminants:
A number of toxic and non-toxic metals occur in the atmosphere. Most of the metals are destructible poisons to living beings, e.g., Cd, Pb, Cr, Be, Ba, Mn etc., which are most toxic.
(vi) Carcinogens:
A group of carcinogens, such as benzidine, β-naphthylamine, vinyl chloride, α-naphthylamine, ethylene dichloride etc. present in air cause cancer in man and animal affecting DNA and cell growth.
(vii) Biological Contaminants:
There exits various air borne microorganisms, pathogens, bacteria, viruses and parasites, which are added as air pollutants in the atmosphere. Other inorganic particles, e.g., flyash, silica, asbestos and dust from transport, mining, metallurgical and other industrial process.
Essay # 5. Air Pollutants Gases:
These pollution causing factors are gaseous in physical state. These gases mix freely with air without settling down.
These are mainly as follows:
(a) Oxides of Nitrogen (NO2 and NO):
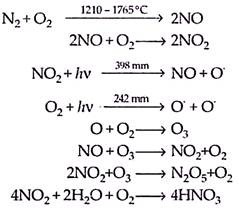
These oxides are produced from acid manufacturing plants, explosive industries, power plants and acid-packing industries. There are eight possible oxides of nitrogen but only NO2 and no are more significant from air pollution point of view. The formation of no from nitrogen is favoured at high temperatures (∼1210 to 1765° C) which are usually obtained in the combustion process involving air.
Rapid cooling of combustion product prevents the dissociation of NO. Further the oxidation of no to NO2 is also favoured at high temperature (∼1100 °C) but the amount of NO2 formed does not exceed from 0.5% of the total nitrogen oxides. NO2 is also formed by photolytic reaction in the atmosphere.
Some of the reactions involved are as follows:
The average lifetime of NO and NO2 is four days and three days respectively in the atmosphere. They undergo various photochemical reactions leading to the formation of HNO3 which gets precipitated as nitrates during rainfall or other natural process. The chemical and photochemical reactions involving NO2 and hydrocarbons induced by sunlight are responsible for the formation of photochemical smog. The nitrogen oxides formed react with organic compounds such as hydrocarbons present in gasoline, in the presence of sunlight, producing peroxyacetylnitrate (PAN), which has formula —
PAN was identified as the major visible toxicant in the photochemical smog.
The formation of smog causes following effects:
(i) Limits the visibility on roads,
(ii) Causes eye irritation,
(iii) Causes difficulty in breathing.
(b) Sulphur Oxides:
The most common type of air pollution from the 14th century to the early twentieth century is from the smoke and gases released by the burning of coal. The lower grades coal contains sulphur in its reduced forms, much of it as iron pyrite, FeS2.Coal (and fuel oils) also contains reduced sulphur in organic forms such as RSH or R-S-S-R, where R represents a complex of carbon.
The sulphur is oxidized to the primary pollutant sulphur dioxide when the fuel is burned:
4FeS2 + 11O2 → 2Fe2O3 + 8SO2
The SO2 formed is eventually oxidized to sulphur trioxide (SO3) by a number of possible reactions whose net result is:
2SO2 + O2 → 2SO3
SO3 combines with water vapours and produces a mist of sulphuric acid:
SO3+ H2O → H2SO4
Reduced sulphuric acid mists are responsible for the bluish haze in atmosphere. The sulphuric acid mist can react with other materials present in the air, such as metal oxide dusts (e.g., CaO), NH3 and salt crystals (NaCl), to form sodium sulphate particulates—
H2SO4+ CaO → CaSO4+ H2O
H2SO4+ 2NH3 → (NH4)2SO4
H2SO4 + 2NaCl → Na2SO4 + 2HCl
Effects:
(i) The presence of the gas causes cardiac and respiratory diseases(e.g. asthma and bronchitis).
(ii) Eye irritation.
(iii) Damage to agriculture.
(iv) Throat troubles and corrosion of metals.
(v) It also affects plant cells in membrane damaging; chlorophyll destruction, metabolism inhibition and growth yield reduction.
(vi) SO3 and SO2 cause a very dangerous effect on living being on earth surface causing acid rain.
(c) Hydrogen Sulphide:
It is produced by the decomposition of sewage wastage or organic matter and as a by-product from various industries. H2S is more poisonous than even carbon monoxide and causes an adverse effect on living as well as on non-living world.
(d) Carbon Monoxide:
It is colourless, odourless and a toxic gas which is slightly water soluble and extremely dangerous due to great affinity for haemoglobin. Carbon monoxide is released by the partial combustion of fuel in automobile industries and oil refineries. Domestic heal appliances, cigarette and bidi smoke are other sources of CO.
It is estimated that the amount of CO liberated every year is about 290 million litres in atmosphere It is corrosive and a very toxic air pollutant. It causes headache, visual irritability, paralysis and even death in human beings. It has 250 times greater affinity for haemoglobin than O2. It forms a stable compound with haemoglobin namely carboxy haemoglobin.
It can be represented as:
The immediate effect of CO poisoning is loss of judgement, which is responsible for many automobile accidents. Further exposure to higher levels of CO leads to various metabolic disorders such as asphyxiation and causes death.
In the study conducted by the National Environment Engineering Research Institute (NEERI), the concentration of carbon monoxide at street level was found to be in the range of 10 ppm to 35 ppm, a value much higher than would be expected from the prevailing traffic density.
(e) Carbon Dioxide:
CO2 is also colourless and odourless in nature. It is discharged into atmosphere in the form of smoke, which is produced by combustion of fuels such as coal, wood, petroleum products and gaseous fuels. It is also released during respiration of plants and animals. The increase in concentration of CO2 in atmosphere causes respiratory disorder and suffocation. CO2 also plays an important role in heating up of environment due to trapping of infrared rays from sun, which is called Greenhouse effect.
(f) Hydrogen Fluoride:
It is released from the industries of phosphate fertilizers, aluminium metallurgical process, brick-kilns, pottery kilns and coal burning industries. It is also produced by automobiles. Due to the presence of this pollutant there are many types of disorders in human body e.g., irritation, skeleton disorders and respiratory diseases. It also causes fluorosis in cattle breeding by using plants affected with HF.
(g) Hydrocarbons:
These are made up of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons, which are volatile in nature, takes part in atmospheric reaction with other organic compounds producing ozone. These hydrocarbons affect human body adversely due to very reactive in nature. Even carcinogenic hydrocarbons like benzopyrenes can react with DNA thus causing mutation and cancer. Inhalation of aromatic hydrocarbon vapour produces more serious ill effects like irritation to muscles, membranes, problems in respiratory system, lungs, cancer and disorders in nervous system and may even lead to death.
Methane is a major naturally occurring hydrocarbon emitted in the atmosphere. It is produced by bacteria during anaerobic decomposition of organic matter in soil, water and sediments—
The evaporation of organic solvents like C6H6, C6H5CH3, CCl4, CHCl3 etc. emit about 10% hydrocarbons in the air during industrial operation. Hydrocarbons enter the atmosphere directly due to petroleum refineries or by evaporation from the fuel tanks of automobiles. Some olefins produced by cracking of saturated hydrocarbons are very harmful-
C8H18(g) → 2C2H4(g) + C4H8(g) + H2(g)
Unsaturated hydrocarbons such as ethylene and butane can react with species such as O, NO or O3 to produce some of the most toxic components of photochemical smog.
(h) Internal Combustion Engines:
When fuel is combusted in an engine different type of air polluting gases and particulate pollutants e.g., Pb etc., are discharged in atmospheric air. The fuels used are the mixture of various hydrocarbons of different molecular masses and formulae. When these are combusted in the internal combustion engine of an automobile in the presence of air, the following reaction takes place-
Hvdrocarbons → x CO2 + y H2O + Heat
Vapours of un-burnt hydrocarbons produce a number of petrochemical oxidants and photochemical smog with O2 and N2 which cause adverse effects on physiological activities of living beings.
Essay # 6. Particulate Pollutants:
The pollutants which are particulate in nature are called particulate pollutants. They exist in particle form in atmosphere, thus causing air pollution.
They are mainly as follows:
(a) Dust:
Dust is composed of fine solid particles and their size ranges from 1 micron to 100 microns. Even dust particles of the size 0.1 micron have been observed in the atmosphere. They are liberated mainly from mines, speeded winds, industrial furnaces, traffics, house cleaning dust, combustion operations, metallurgical processes and many other activities taking place in the era of the industrialization. Dust makes the atmospheric air unfit for respiration.
Atmospheric dust causes allergic and respiratory diseases; if it possesses silica then it causes silicosis.
(b) Radioactive Gases and Dust:
The radioactive gases are liberated from natural and artificial radioisotopes. These get mix with dust. They cause leukemia, cataract, cancer and affects human being genetically such as mutation in human gametes.
(c) Lead (Pb):
It is discharged from automobile emission; burning of coal, lead arsenate pesticides and lead smelters. It causes respiratory, excretory disorders, liver and kidney damage and mental retardation in children. Lead content in human blood exceeding 40 ppm is considered to be dangerous. Tetra Ethyl Lead (TEL) is more harmful than inorganic lead.
According to Vincent J. Schaefer, Head of the Atmospheric Science Research Centre of New York State University, over seeding of clouds is caused by extremely tiny crystals of lead iodide, formed from tiny particles of lead released from tetraethyl and traces of iodine in the atmosphere. The decline of rain and snowfall would be serious enough to upset the equilibrium that exists between air, water and the earth, if automobiles continue to use leaded gasoline.
(d) Mercury (Hg):
The main sources of Hg particles are mining and refining of mercury. Pure mercury is not particularly toxic and inhalation of a very small amount of Hg does not produce any ill effect. Hg vapours are very dangerous, it cause irritation, destruction of lung tissues, protoplasmic poisoning. Organomercuric compounds are highly toxic and may cause irreversible damage to nervous system and brain.
(e) Cadmium (Cd) and Arsenic (As):
They are discharged in atmosphere as byproducts of Pb, Zn and Cu metallurgy, nuclear fission plants, Cd-Ni batteries, Cd producing industries. Inhalation of Cd fumes causes kidney damage, bronchitis, gastric disorders, cancer and heart diseases. Arsenic is liberated from fungicides, pesticides, byproduct of mining activities and chemical grades.
(f) Smoke and Fumes:
Smoke particulates consist of solid and liquid particles ranging from 0.05 to 1.0 microns which are formed during incomplete combustion of carbon containing materials. It includes smoke of gaseous pollutants like oxides of nitrogen, carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons etc.
Fumes are generally obtained by the condensation of vapours by sublimation, distillation, boiling, calcinations and by several other chemical reactions. Generally organic solvents, metals and metallic oxides form fume particles having a size less than 1 micron.
(g) Mist and Spray:
Mist or liquid particles are formed by condensation of vapour, having a size less than 10 µ, e.g.
Spray constitutes liquid particles obtained from the parent liquid by the process of mechanical disintegration.
Essay # 7. Effects of Air Pollution on Humans:
The effects of air pollution on humans are fatal and life threatening. WHO statistics report that over 2 million people succumb to the fatalities attributed to air pollution.
Consistent exposure to the pollutants leads to the development of:
(i) Cardiopulmonary disease
(ii) Pneumonia
(iii) Premature mortality
(iv) Heart attack
(v) Asthma
(vi) Difficulty in breathing
(vii) Wheezing and coughing
(viii) Acute vascular dysfunction
(ix) Thrombus formation
(x) Cystic fibrosis
(xi) Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
(xii) Chronic bronchitis
(xiii) Emphysema.
There are a number of ways, by which these emissions could be controlled. Particulate control is possible with the use of mechanical collectors, electrostatic precipitators, bag-houses and scrubbers like the Baffle, Cyclonic, Ejector venturi and Mechanical scrubbers.
Nitrogen dioxide control is possible with the help of low consumption burners and scrubbers, selective catalytic and non- catalytic reduction and even catalytic converters. Sulfur dioxide or acid gas can be effectively controlled with dedicated use of wet and dry scrubbers and the latest introduction of flue gas desulfurization.
The world’s most polluted cities include Australia, America, the UK, China and India as forerunners. The greenhouse effect is a life threatening global phenomenon that is the creation of air pollutants. This phenomenon is the result of the trapped greenhouse gases in the upper atmosphere.
Accumulation of carbon dioxide gas, methane, nitrogen oxides, hydrofluorocarbons, perfluorocarbons and chlorofluorocarbons have brought on a major climate change, increased acidity of ocean waters and major modifications in marine ecosystems.
Essay # 8. Prevention of Air Pollution:
How You Can Help to Prevent Air Pollution:
(i) Carpool — This will help to reduce the number of vehicles on the already congested roads.
(ii) Always keep your car tuned properly so that it remains in a good condition.
(iii) Save energy — Try to use minimum amounts of natural gas and even electricity. Whenever possible, avoid the use of air conditioner and use a fan instead.
(iv) Always buy recycled products.
(v) Reuse things such as paper and plastic bags, paper etc. This will contribute a lot towards reducing the effects of air pollution and global warming.
(vi) Avoid the use of firecrackers. You don’t really need it to express your feeling of happiness.
(vii) Go in for water-based paints instead of varnishes.
(viii) If you really cannot avoid using your can plan your work systematically to reduce air pollution.
Air pollution being a serious problem, should be checked at any cost. There are a number of methods by which we can control and prevent air pollution up to a great extent.
These are as follows:
1. The minimization of automobile emission should be carried out by cleaning exhaust gases with the help of catalysts.
2. The chimney in various industries causing air pollution as in power plants, brick manufacturing plants etc. should be very high so that pollutant gases may reach to the upper level of atmosphere far from the ground level. The pollutant minimizing devices should be applied in these chimneys or stacks so that the amount of polluting gases e.g. SO2 etc. can be reduced within the chimney.
3. Deforestation should be checked strictly and programmes of plantation should be encouraged. Besides absorbing CO2, many plants are capable of absorbing significant amount of hydrogen sulphide and nitric acid. In the absence of trees and green vegetation air becomes richer with harmful pollutants like NxOy, H2S and O3, thus causing air pollution.
4. SO2 formation by combustion processes can be controlled by desulphurization of fuel. SO2, and acid fumes can be removed by passing the stack or fuel gases through a bed of alkaline alumina, activated carbon or limestone powder where SO2 etc. are absorbed.
5. The use of power generating devices such as coal and wood combustion should be reduced in domestic as well as industrial activities. In place of these, modern power generating devices should be used which are electricity, solar energy, nuclear power plants which will help in reducing air pollution.
6. Industries should be established at a sufficient distance from populated area so that air- polluting gases may get diluted in the atmosphere before reaching to populated area. This process is known as zoning or buffer zoning.
7. Clause Process- It is a method used for controlling the pollution caused by H2S and SOx, which are liberated by refineries. The result of this process is the formation of elemental sulphur as a byproduct.
It is a two-stage process, which occurs, in the following two steps:
2H2S + 3O2(g) → 2H2O + 2SO2
2H2S + SO2 → 2H2O + 3S
8. Acids and chemical fumes are removed by passing gases and vapours through a tower filled with coke and a water counter current is applied against it. By this method we can recover the useful volatile substances simultaneously, which have commercial values.
9. Smoke concentration can be reduced by maintaining high temperature during the combustion of fuel and feeding of fuel continuously. Installation of Cottrell electrostatic precipitator minimizes the smoke quantity.
10. Extraction ventilations are more frequently applied for the removal of dust from air. In this process firstly a stream of air carrying suspended dust particles is maintained at a sufficient velocity to keep the dust in suspension and secondly the rate of the stream is reduced suddenly to some extent to cause the dust particles to settle down in a settling chamber. Thus air is made dust free by the process.
11. Air pollution can be controlled by using cyclone collector. This equipment is usually used as a pre-cleaner of air. The principle of this equipment is that the particulate matter present in air possesses greater moment of inertia than that of gases and fumes. In cyclone collector, moment of inertia of particulate is less than that of gases and fumes.
In cyclone collector, the smoke or gas containing particulate is allowed to flow into a tight circular spiral fitted chamber. Inside the cyclone there is a device to rotate the fume at a desired speed. The particulates in air feel greater inertial effect, being heavier particle, due to centrifugal force.
Consequently these particles tend to move away from the centre towards the wall of chamber from where they start to settle down due to force of gravity. Thus particulate so gathered at the bottom of chamber are removed periodically.
12. Air pollution can be controlled by fuel selection and better utilization. Windmills and other such sources of power and fuel should be used. The aim is to generate power without burning fossil fuels which emit CO2.
Essay # 9. Air Pollution Control Equipment:
Here are a few air pollution control systems that are being used by vehicles and industries. They help to either remove pollutants from a stream of exhaust before they are emitted into the air or destroy them.
Air Pollution Control Systems to Reduce Particulate Matter:
i. Wet Scrubbers:
These include a number of devices that remove pollutants from furnace flue gas as well as other gas streams. The pollutants are removed by the polluted gas stream being forced through a scrubbing liquid or by using some other method of bringing it into contact with the liquid. Wet scrubbers are used in a number of industries like large power plants, asphalt plants, steel plants, fertilizer plants, and acid plants.
ii. Electrostatic Precipitator (ESP):
Also known as Electrostatic Air Cleaners, this air pollution control system is a particulate collecting device which uses the force created by an induced electrostatic charge to remove particulate matter from any flowing gas, e.g., air. These filtration devices are highly efficient and are very effective in removing fine particles like smoke and dust from the air stream. ESPs are used for controlling particulate emissions in various industries like oil refineries, pulp mills, and oil and coal fired utilities that generate electricity which produce smoke.
iii. Dust Cyclones:
These are used to remove particulate matter from a gas or air stream, without using filters, using vortex separation instead. Mixtures of fluids and solids are separated by using gravity and rotational effects. There is large scale use of cyclones in oil refineries as well as the cement industry wherein they form a part of the kiln preheaters.
Air Pollution Control Systems to Reduce NOx (Nitrogen Dioxide and Nitrogen Oxide):
i. Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR):
This is a technique used for reducing NOx that is used in most diesel and gasoline engines. A part of the exhaust of an engine is re-circulated back into its cylinders. When the incoming air is intermixed with the re-circulated exhaust gas, it results in diluting the mixture with inert gas, reducing the adiabatic flame temperature and also lowering the excessive oxygen in diesel engines.
The peak combustion temperature is also lowered because the specific heat capacity of the mix is increased by the exhaust gas. Since high temperatures cause Nox to form much faster, EGR helps in limiting NOx from being generated. Nox is produced when a mixture of oxygen and nitrogen is subjected to high temperatures.
ii. Catalytic Converter:
This is a device that is used to diminish the toxicity of emissions that are produced by internal combustion engines. First introduced in 1975 in the US in order to comply with the tightening regulations by the Environmental Protection Agency, catalytic converters are still used most commonly in the exhaust systems of motor vehicles. Some of the other places they are use in are- trains, mining equipment, forklifts, generator sets, and other machines equipped with engines.
Air Pollution Control Systems to Decrease Volatile Organic Compounds (VOC):
i. Gas Flare:
Also called a flare stack, this is a chimney that is erected on oil rigs or oil wells, as well as landfills, chemical plants, and refineries. When flammable gas or unusable waste gas plus liquids are discharged by pressure relief valves, this device is used to burn them off. This device is also used in landfills to burn and/or vent the waste gas that is produced by the decomposing materials.
ii. Biofilters:
This is a technique for pollution control which uses living matter to trap and biologically degrade pollutants. In air pollution control, the pollutants in the air are subjected to microbiotic oxidation. In other words, when it is applied in the filtration and purification of air, microorganisms, such as fungi and bacteria that are embedded in a biofilm, are used to degrade the air pollutant.