Here is an essay on ‘Vegetables’ for class 5, 6, 7 and 8. Find paragraphs, long and short essays on ‘Vegetables’ especially written for school and college students.
Essay on Vegetables
Essay Contents:
- Essay on the Introduction to Vegetables
- Essay on the Characteristics of Vegetable
- Essay on the Scope of Vegetable
- Essay on the Varieties and Hybrids of Vegetables
- Essay on the Area and Production of Vegetables
- Essay on the Importance of Vegetable Production
- Essay on the Classification of Vegetable
- Essay on the Different Types of Vegetables Farming
Essay # Introduction to Vegetables:
The term ‘Vegetable’ includes all foods of vegetable origin, but it excludes cereal and dried seeds of pulses, it includes grain on the cob, potatoes and other tubers. Vegetables are an integral part of human diet and known as protective foods, which contribute required minerals, vitamins and other nutrients of medicinal and therapeutic values.
Olericulture is derived from two words, i.e., ‘Oleris’ meaning ‘potherb’ and ‘culture’ meaning ‘cultivation’. So, olericulture literally means potherb cultivation. In present day, it is broadly used to indicate the cultivation of vegetables.
It is any part of the herbaceous plant that is generally used after cooking as a principal part of the meal. Vegetables are called protective food as their consumption can preventive several diseases. Vegetable plays an important role in the balanced diet by providing not only energy, but also supplying vital protective nutrients like-minerals and vitamins.
Essay # Characteristics of Vegetable
:
Vegetables form an indispensable part of daily diet particularly in India, as a large section of people are vegetarian. So, for fulfilling the dietary requirements they depend on vegetables.
Vegetables are important for our well-being because of the following:
(i) Vegetables are rich sources of vitamins and other essential nutrients.
(ii) Vegetables play an important role in human diet and are essential for balanced diet and maintenance of good health.
(iii) The vegetables are rich sources of protein (moringa and peas), minerals like calcium (tomato, spinach, peas), phosphorus (tomato, cucumber), iron (spinach, peas, tomato, bitter gourd), iodine (okra, summer squash) vitamins like vitamin-A (leafy vegetables, pumpkin), vitamin-B (peas, spinach, tomato), vitamin-C (moringa, chilli, tomato,) and vitamin-K (leafy vegetables).
(iv) Vegetables have lots of protective compounds like cheratin in bitter gourd is effective against diabetes and most of the leafy vegetables and pumpkin are the rich source of beta carotene.
(v) Vegetables gave more yield than other traditional crops like wheat and rice. The yield of wheat is about 50-55 quintal/hec and in vegetables like tomato it is about 250 quintal/hec. Thus, they provide higher quantity of food per unit area.
(vi) Vegetables gave more farm income than other crops.
(v) The cropping intensity in vegetable growing is very high as compared to others.
(viii) Normally, 3-4 vegetable crops can be raised in one year.
(vi) Vegetables have high export potential.
(vii) The aesthetic value of vegetables is quite higher than other field crops.
Essay # Scope of Vegetable
:
In a vast country like India there is an immense scope of vegetable cultivation as mentioned below:
(i) Sufficient technical manpower is available in our country and apart from it; there are many unemployed agriculture graduates and postgraduate degree holders.
(ii) There are varying agro-climatic conditions temperate to subtropical, in different regions of the country and variety of vegetables can be grown all over the country.
(iii) There is abundance of rainfall and no scarcity of water for vegetable cultivation. There is large scope for area expansion under vegetable crops.
(v) There is high potential for high value low volume crops as purchasing power of lot of population in India is very high.
(vi) In India, the market for processed vegetables is increasing and thus more vegetable production is needed.
Essay # Varieties and Hybrids of Vegetables
:
Many varieties of various vegetables according to size, shape, colour, yield. etc., are grown throughout the country.
The important varieties and hybrids are as follows:
Arka Saurabh, Arka Vikas, Pusa Uphar, Hisar Anmol, Hisar Arun, Hisar Lalit, La-Bonita, Pant Bahar, Punjab Chhuhara, Avinash-2, Punjab Kesri, Pusa Early Dwarf, Pusa Ruby, Pusa Sheetal, Roma, Sel 120, Hisar Lalima, Krishna, Matri, Naveen, Pusa 120, Pusa Divya, Pusa Gaurav, Pusa Sadabahar, Rajni, Rashmi, Ratna, S-12, Pant T-3, BT-1, CO-3, KS-2, NTLDR-1, PKM-1, Punjab Tropic, PNR-7, TH-2312 and TH-802.
Pusa Purple Long, Pusa Anupma, Arka Kusumkar, Jamuni Gola, Pusa Purple Cluster, Arka Navneet, Arka Sheetal, Arka Shirish, Manjari Gota, Mysore Green, Annamalai, Pant Samart, Pusa Kranti, Pusa Bhairav, Pusa Anupam, Pusa Upkar, Pusa Bindu, Punjab Barasti, Pant Rituraj, Aruna, Punjab Neelam, Punjab Sadabahar, Punjab Moti, BH-1, BH-2, Azad Kranti, Hisar Jamuni and Pragati Arka.
Pusa Jwala, Bhagyalakshmi, Andhra Jyoti, Sindhur, Punjab Lal, Bhaskar, Co-1, Co-2, Arpana Jawahar-218, Pusa Sadabahar, Arka Lohit, Arka Abir, Bhaskar, Masalwadi Selection, CH-1, CH-3, Punjab Gucchedar, Punjab Surkh and Ujjwala.
California Wonder, Arka Mohini, Arka Gaurav, Arka Basant, Pusa Green Gold, Indira, Hira, Pusa Sanyog and Kt-I.
Essay # Area and Production of Vegetables
:
India is the world’s second largest producer of vegetables next only to China.
Present productions of vegetable not meet the requirement of 300 g vegetable per head per day, so, there are require more production.
Essay # Importance of Vegetable Production
:
The importance of vegetables production is discussed below:
1. Importance of Vegetables in Human Nutrition:
Vegetables are very important in our daily diet. Both our diet and the economic position can be improved by growing more vegetables throughout the year. Vegetable is a good source of roughages, which promote digestion and helps to prevent constipation and also they are rich sources of minerals, carbohydrates, vitamins and proteins.
(i) Minerals:
At least ten mineral element needs for proper growth and development of our body. Out of these, calcium, phosphorus and iron are required in large quantities, which are lacking in cereals and are available abundantly in vegetables like, e.g., peas, beans, spinach, cabbage, cauliflower, tomato, lettuce, etc.
(ii) Carbohydrates and Proteins:
Vegetables in general are not considered of great importance in furnishing carbohydrates, proteins and fats. But some of them such as dried seeds of beans, peas and lentils are rich in protein and potatoes, sweet potatoes and carrots are important sources of carbohydrates.
(iii) Vitamins:
Vitamin has a key role in the development of the body and requires in small quantity. All the vitamins are found in small or large quantities in most of the green vegetables.
(iv) Bases for Neutralisation:
Calcium, magnesium and potassium are the most important bases needed for neutralising the acid produced in the body during the digestion of meat, cheese and other fatty acids and they are available from vegetable food.
Because of their high yielding and short duration characteristics, vegetables form a chief source of income to the farmers.
(i) Important Source of Farm Income:
Vegetables are sold at a higher rate than other crops. It provides regular as well as good source of income in addition to the income from the agronomical crops. It provides regular work throughout the year to the farmers and his family laborers. It supplies food stuff to his family and fodder in the form of refuse to his cattle. It provides better utilisation of land, labour and capital.
(ii) High Yielding:
Vegetables give very high quantity of food per acre and they grow quickly. It is found that vegetables give higher yields in comparison to other crops. It helps to follow crop rotation and mixed cropping system in his land. The farmers thereby maintain the soil fertility which aids in higher yield.
(iii) Short Duration in Nature:
Most vegetables are short duration crops and they as compared to other crops, can be raised throughout the year. Some of vegetables (like potato, brinjal, spinach, pumpkin, lady’s finger, etc.) can be grown twice and even thrice a year. Some green vegetables become ready for harvesting within 15 to 60 days of sowing. It is possible to cultivate several vegetables one after the other throughout the year, if irrigation facilities are available. Vegetables can be cultivated even in smaller plots.
Many of the vegetable crops possess high medical value for curing certain diseases. For instance, onion and garlic are found to possess anti-bacterial property and are also involved in lowering the raising blood sugars. Brinjal is found to be useful against diabetes. Many solanaceous and cucurbitaceous vegetables are found to possess vitamin-D component, B- carotene, saturated fatty acids and sugar constituents, which have therapeutic value.
4. Aesthetic Value of Vegetables:
Kitchen garden or vegetable garden adds aesthetic value to the houses. A piece of land adjoining the house, if worked well with a little effort will produce many vegetables without difficulty, by which a lot of saving can be made on this item in the expenditure. Only those who have caused a seed to sprout in the soil can fully comprehend the glory of the act. Even a kitchen garden or any garden can give him the joy and aesthetics of cultivation.
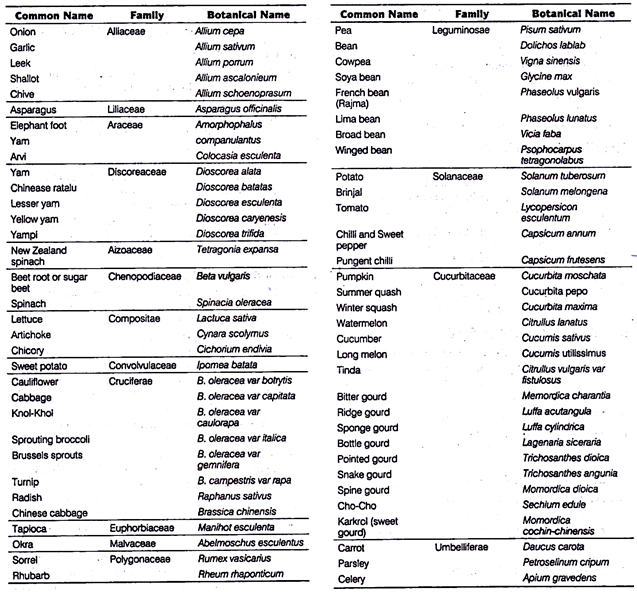
Essay # Classification of Vegetable:
1. Botanical Classification:
2. Based on Temperature Tolerance:
(i) Cools Season Crop Hardy – Asparagus, broccoli, brussels sprout, kale, kholrabi, leek, onion, pea, radish, turnip, spinach, mustard, rutabaga, etc.
Half Hardy – Beet, carrot, cauliflower, celery, chard, Chinese cabbage, lettuse, potato, parsnip, jerusalem artichoke, globe artichoke, etc.
(ii) Warm Season Tender – Cowpea, snap bean, soya bean, tomato, sweet corn.
a. Very Tender – Cucumber, cantaloupe, eggplant, okra, pepper, pumpkin, squash, sweet potato, watermelon, etc.
b. Immature Fruit – Cucumber, eggplant, okra, sweet corn, snap bean, summer squash.
c. Mature Fruit – Muskmelon, cantaloupe, pepper, pumpkin, tomato, watermelon, potato, podded pea, and winter squash.
d. Seed – Cowpea, garden pea, soya bean, limabean.
3. Classification by Life Cycle:
(i) Annual Vegetables – Cowpea, cucumber, cantaloupe, okra, pea, lettuce, pumpkin, snap bean, soya bean, spinach, squash, sweet corn, watermelon, potato, broccoli, cauliflower, Chinese cabbage.
(ii) Biennials – Beet, broccoli, brussels sprout, cabbage, carrot, cauliflower, celery, chard, collard, kale, leeks, onion, turnip, parsnip, kohlrabi, Chinese cabbage.
(iii) Perennials – Asparagus, eggplant, garlic, globe artichoke, jerusalem, artichoke, lima bean, pepper, potato, tomato, sweet potato, rhubarb.
4. Based on Parts Used as Food:
(i) Leafy Vegetable – Palak, Amaranthus, portulacaceae, bathua, lettuce, tender gram, mustard, pea twings, cabbage, brussels sprout, collard, kale, chard, celery, Chinese cabbage, etc.
(ii) Stem Vegetables – Potato, kholrabi, Asparagus.
(iii) Root Vegetables – Potato, sweet potato, elephant foot yam, yam, tapioca yam, carrot, radish, turnip, Parsnip.
(iv) Bulb Vegetables – Onion, garlic.
(v) Fruit Vegetables – Tomato, brinjal, sweet pepper, beans, cucurbits, okra.
(vi) Flower Vegetables – Cauliflower, broccoli, globe artichoke.
5. Based on Methods of Raising:
(i) Direct Sown – Okra, carrot, pea, garlic, beans, radish.
(ii) Transplanted Crops – Brinjal, chillis, tomato, cabbage, cauliflower.
6. Based on Tolerance to Soil Acidity:
(i) Slightly Tolerant – (Okra, cabbage pH 6.8 to 6.0) Cauliflower, onion, muskmelon, palak, lettuce, leek, spinach, Asparagus, broccoli, beet.
(ii) Moderately Tolerant – (pH 6.8 to 5.5) Brinjal, pea, pumpkin, garlic, knol-khol, turnip, cucumber, squash.
(iii) Very Tolerant – (pH 5.5 to 5.0) Sweet potato, potato, watermelon, rhubarb.
Essay # Different Types of Vegetables Farming
:
Kitchen gardening is the growing of vegetables crops in the residential houses to meet the requirements of the family all the year round. It aims at an efficient and effective use of land for growing essential vegetables for daily use of family.
Kitchen garden should aim at giving a continuous supply of vegetables to the family throughout the year, according to season. Most of the work is done by the family members in spare time. The land is selected usually in the back yard of the house, where possibly a rectangular piece of land rather than a square is preferable.
Market gardening is a branch of vegetable fanning, which produces vegetables for supply to the consumer in the local market. Generally, market gardens are located within a distance of 10-20 km from the cities. But with the increase in communication and transport facilities, it is not unusual to find such gardens even beyond 30-40 km from the city, where produce can be marketed daily.
Selecting a site for the market gardens the following points should be taken into consideration – Topography, soil character, climatic condition, availability of labour, nearness to market, transport facility, irrigation facilities, etc.
The word Truck has been derived from a french word troquer, which meant to barter. This is the extensive type of gardening where the grower specialises in one or two crops, the produces special crops in larger quantities for distance markets.
Only few vegetables which can sustain long distance transport without any damage or deterioration, i.e., potato pumpkin, chillies, onion, etc., are suitable for truck gardening.
4. Gardens for Vegetables Forcing:
This type of farming is adopted to grow vegetables out of normal season and is widely prevalent in USA, UK and other Western countries, because the environmental factors are not always favourable for growing all the vegetables in open throughout the year.
Vegetables forcing requires some special structures like greenhouse, glass house, hot bed and cold frame. These structures may be permanent or temporary and erected, where electricity and water are easily available.
Most forcing house crops need fertilisation particularly for cucumbers, tomatoes and melons. Mostly liquid fertiliser is popular in forcing
5. Garden for Vegetable Processing:
The type of farming which produces vegetables or their cultivars with a sole objective of supplying them to the processing factories is termed as vegetable forcing.
Tomatoes, peas, snap melon are good for canning. Broccoli, spinach, lima bean are suited for freezing. White cultivars of onion and potatoes are suitable for dehydration.
This garden is generally found in the Lakes of Kashmir valley. First of all, a floating base is prepared with some grass known as Typha, which is grown wild in those areas. After that compost and other organic matters are spread over it and seedlings are transplanted. Most of the vegetables are supplied in Kashmir from this type of garden.